Developing a Custom chart
Introduction
Custom Charts enable you to develop your own specialized data visualizations and connect them to Luzmo , allowing you and your users to easily add them to Luzmo dashboards. If our built-in chart types don't fully cover your specific visualization needs, you can create custom charts tailored exactly to your requirements.
Why use Custom Charts?
Complete visualization flexibility: Design exactly the chart types your data or use case needs, ensuring your end-users get precisely the visualization experience required.
Efficient implementation: Write only your visualization code and let Luzmo do the rest — querying, filtering and interactivity is all handled for you. Maintain complete control over your visualization UI/UX while leveraging Luzmo's powerful analytics infrastructure.
Full integration with Luzmo's capabilities : Your custom charts seamlessly integrate into Luzmo dashboards.
We provide a Custom Chart Builder that provides a complete development environment for building, testing, and packaging custom chart components.
Key features of the custom chart builder environment:
Interactive development environment with live preview
Configurable data slots for chart customization
Automatic build and refresh on code changes
Schema validation for chart configuration
Production-ready packaging tools
Quick Start
Prerequisites
Node.js (v16+)
npm
Installation
Clone the custom chart builder repository from our GitHub:
bashgit clone https://github.com/luzmo-official/custom-chart-builder.git cd custom-chart-builderInstall dependencies:
bashnpm installStart the custom chart builder development environment:
bashnpm run start
The development environment will be available at http://localhost:4200 .
Once it's up and running, log in to the environment with your Luzmo account. This will bring you to the builder environment. The page features 3 areas:
Dataset selection : open the dropdown to select one of your datasets to show its columns.
Chart slots : this area shows a visual representation of the chart slots you defined in your
manifest.json. Changes to the manifest will be reflected in this area. Columns can be dragged to these chart slots. Once all required slots are filled, a Luzmo query will execute and show you the returned data. This gives you useful information about the shape of the data you'll be working with in your visualization code.Chart visualization : this area executes the
rendermethod of your chart code with the data returned by the query. It shows you how your custom chart will look in your dashboards, based on your current code.
Project structure
custom-chart-builder/
├── custom-chart-build-output/ # Production build files
├── projects/
│ ├── builder/ # Angular application for the chart builder UI
│ └── custom-chart/ # Your custom chart implementation
│ └── src/
│ ├── chart.ts # Main chart rendering logic
│ ├── chart.css # Chart styles
│ ├── manifest.json # Chart configuration and slot definitions
│ ├── icon.svg # Chart icon
│ └── index.ts # Entry point Your main working directory will be the projects/custom-chart/src directory, where your custom chart implementation is located.
Creating your custom chart
Let's dive into the process of implementing your own custom chart.
Key files to modify
To create your own chart, you'll primarily need to edit these three files:
manifest.json - define your chart's data slots and configuration.
chart.ts - this is where you'll implement the chart rendering logic.
chart.css - add styles for your chart's visual appearance.
Manifest configuration
The manifest.json file defines the data slots of your custom chart. A data slot can receive one or multiple columns from your datasets. These slot definitions determine what type of columns are accepted by your chart and how these options are displayed in Luzmo's editor. Based on the slot definitions, Luzmo will automatically generate and update queries to retrieve data in the format expected by your chart once all required slots are filled.
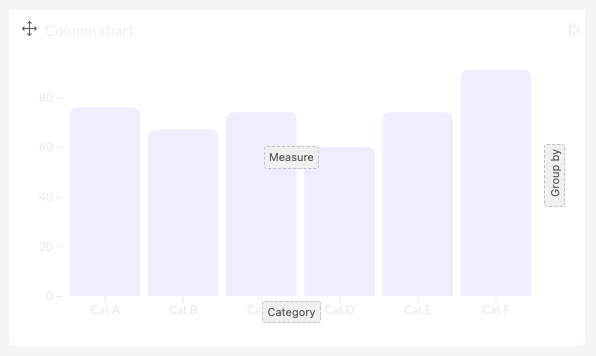
For example, Luzmo's built-in column chart has 3 slots: "Measure", "Category", and "Group by". As set in the slot definitions, the "Measure" slot will accept multiple columns, while the "Category" column will only accept one column. When the "Measure" slot contains more than 1 column, the "Group by" slot must be empty, and vice-versa.
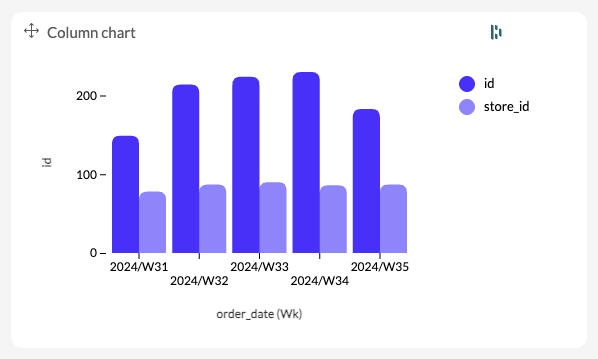
When a user adds columns to the chart, Luzmo will automatically retrieve the aggregated data, respecting any applied filters. In the example below, Luzmo will query the unique id's and unique store_id's, aggregated by week, from a dataset containing ecommerce orders. When developing the chart, that's the data you'll have to visualize.
Required properties
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
name STRING |
Internal identifier for the slot. Note: within one chart, all slots must have unique names! Must be one of:x-axis, y-axis, category, measure, coordinates, legend, geo, image, color, levels, slidermetric, dimension, destination, source, time, identifier, target, size, name, columns, column, row, evolution, close, open, low, high, order, route
|
|
label STRING |
User-facing name displayed in the interface. Can be a string or a record object for localization. |
Optional properties
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
description STRING |
Short explanation of the slot's purpose. |
|
type STRING |
Data type. Must be 'categorical' or 'numeric'. If set to 'categorical', columns in this slot will be added to the dimensions part of the query. If set to 'numeric', columns in this slot will be added to the measures part of the query. This is used to determine how data is aggregated.
|
|
rotate BOOLEAN |
Whether the axis should be rotated. |
|
order NUMBER |
Display order in the interface. |
|
isRequired BOOLEAN |
Whether the slot must be filled. |
|
acceptableColumnTypes ARRAY |
Array of allowed column types. Must be one of: 'numeric', 'hierarchy', 'datetime', or 'spatial'.
|
|
acceptableColumnSubtypes ARRAY |
Array of specific column subtypes. Must be one of: 'duration', 'currency', 'coordinates', or 'topography'.
|
|
canAcceptFormula BOOLEAN |
Whether this slot can accept a formula-based column. |
|
canAcceptMultipleColumns BOOLEAN |
Whether multiple columns can be placed in this slot. |
|
requiredMinimumColumnsCount NUMBER |
Minimum number of columns required. |
|
isHidden BOOLEAN |
If true, this slot won't appear in the UI. |
|
noMultipleIfSlotsFilled ARRAY |
Array of slot names that prevent multiple columns when filled. |
|
options OBJECT |
Additional options for the slot. See table below for more details. |
Slot options properties
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
isBinningDisabled BOOLEAN |
Disable binning for categorical fields. |
|
areDatetimeOptionsEnabled BOOLEAN |
Enable date/time-based options. |
|
isAggregationDisabled BOOLEAN |
Disable aggregation functions. |
|
areGrandTotalsEnabled BOOLEAN |
Enable grand totals. |
|
showOnlyFirstSlotGrandTotals BOOLEAN |
Only show grand totals for first slot. |
|
isCumulativeSumEnabled BOOLEAN |
Enable cumulative sum calculations. |
|
showOnlyFirstSlotContentOptions BOOLEAN |
Only apply content options to first slot. |
Example Manifest
Here's a complete example of a manifest.json file for a basic column chart:
{
"slots": [
{
"name": "category",
"rotate": false,
"label": "Category",
"type": "categorical",
"order": 1,
"options": {
"isBinningDisabled": true,
"areDatetimeOptionsEnabled": true
},
"isRequired": true
},
{
"name": "measure",
"rotate": true,
"label": "Value",
"type": "numeric",
"order": 2,
"options": {
"isAggregationDisabled": false
},
"isRequired": true
},
{
"name": "legend",
"rotate": false,
"label": "Legend",
"type": "categorical",
"order": 3,
"options": {
"isBinningDisabled": true
},
"isRequired": false
}
]
}During the build process, this manifest is automatically validated against the Zod schema. You can also run:
npm run validate to check the validity of your manifest.json against the Zod schema without performing a full build.
Chart implementation
Core functions
To create a working Luzmo custom chart, you'll need to implement at least the render and resize functions.
You can also implement the buildQuery function to create a custom data query if your chart requires it. If your chart does not require a custom data query, you can omit this function entirely and a Luzmo query will be automatically generated based on your slot configurations.
You can find these methods in the chart.ts file, located in the projects/custom-chart/src directory.
render function
The render function is the main function that will be called by Luzmo to initially create and render your chart. It will receive a ChartParams object as a parameter, which contains the following properties:
interface ChartParams {
container: HTMLElement; // The DOM element where your chart will be rendered
data: any[][]; // The data rows from the server
slots: Slot[]; // The filled slots with column mappings
slotConfigurations: SlotConfig[]; // The configuration of available slots
options: Record<string, any> & { theme: ThemeConfig }; // Additional options passed to the chart
language: string; // Current language code (e.g., 'en')
dimensions: { // Width and height of the chart container in pixels
width: number;
height: number;
};
}
export function render({
container,
data = [],
slots = [],
slotConfigurations = [],
options = {},
language = 'en',
dimensions: { width = 600, height = 400 } = {}
}: ChartParams): void {
// 1. Clear the container
container.innerHTML = '';
// 2. Check if data exists
const hasData = data && data.length > 0;
// 3. Extract and process data
const chartData = hasData ? data.map(row => ({
category: String(row[0]?.name?.en || row[0] || 'Unknown'),
value: Number(row[1] || 0)
})) : [];
// 4. Create visualization (SVG, Canvas, etc.)
const svg = d3.select(container)
.append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height);
// 5. Add your chart elements here...
// 6. Store state for resize
(container as any).__chartData = chartData;
}resize function
The resize function is called when the chart is resized. It will receive a ChartParams object as a parameter, which contains the following properties. The dimensions property will contain the new width and height of the chart, which you can use to update the sizes of the elements in your chart.
export function resize({
container,
slots = [],
slotConfigurations = [],
options = {},
language = 'en',
dimensions: { width = 600, height = 400 } = {}
}: ChartParams): void {
// Implementation here
}buildQuery function (optional)
The buildQuery function takes the slot configurations and filled slots and uses them to create a Luzmo data query that fetches the appropriate data.
IMPORTANT: The
buildQuery()method is completely optional. If you don't implement this method, Luzmo will automatically generate and run the appropriate query for your chart based on the slots configuration. You only need to implement this method if you want to customize the query behavior.
For a full reference of the available query parameters, see the Luzmo Query Syntax Documentation .
Example implementation:
interface BuildQueryParams {
slots: Slot[];
slotConfigurations: SlotConfig[];
}
export function buildQuery({
slots = [],
slotConfigurations = []
}: BuildQueryParams): ItemQuery {
const dimensions: ItemQueryDimension[] = [];
const measures: ItemQueryMeasure[] = [];
// Extract category dimension
const categorySlot = slots.find(s => s.name === 'category');
if (categorySlot?.content.length! > 0) {
const category = categorySlot!.content[0];
dimensions.push({
dataset_id: category.datasetId || category.set,
column_id: category.columnId || category.column,
level: category.level || 1
});
}
// Extract measure
const measureSlot = slots.find(s => s.name === 'measure');
if (measureSlot?.content.length! > 0) {
const measure = measureSlot!.content[0];
// Handle different types of measures
if (measure.aggregationFunc && ['sum', 'average', 'min', 'max', 'count'].includes(measure.aggregationFunc)) {
measures.push({
dataset_id: measure.datasetId || measure.set,
column_id: measure.columnId || measure.column,
aggregation: { type: measure.aggregationFunc }
});
} else {
measures.push({
dataset_id: measure.datasetId || measure.set,
column_id: measure.columnId || measure.column
});
}
}
return {
dimensions,
measures,
limit: { by: 100 }, // Limit to 100 rows for performance
options: {
locale_id: 'en',
timezone_id: 'UTC',
rollup_data: true
}
};
}Data formatting
Luzmo provides a powerful formatter utility that helps format your data based on the format configured for the column (which can be changed by the user in the dashboard editor). You can import this utility from @luzmo/analytics-components-kit/utils :
import { formatter } from '@luzmo/analytics-components-kit/utils';It takes a slot content (i.e. a column) as an argument and returns a function that formats the data based on the format configured for the column.
The formatter function automatically handles:
Number formatting (thousands separators, decimal places)
Date/time formatting
Currency formatting
Percentage formatting
Example usage in your chart:
import { formatter } from '@luzmo/analytics-components-kit/utils';
export function render({ data, slots }: ChartParams): void {
// Create formatters for your slots
const measureFormatter = slots.find(s => s.name === 'measure')?.content[0]
? formatter(slots.find(s => s.name === 'measure')!.content[0])
: (val: any) => String(val);
const categoryFormatter = slots.find(s => s.name === 'category')?.content[0]
? formatter(slots.find(s => s.name === 'category')!.content[0])
: (val: any) => String(val);
const categoryValue = row[0]?.name?.en || row[0] || 'Unknown';
const formattedCategory = categoryFormatter(
categorySlot.content[0].type === 'datetime'
? new Date(categoryValue)
: categoryValue
);
// Use the formatters
const formattedData = data.map(row => ({
category: formattedCategory,
value: measureFormatter(row[1])
}));
}Chart styling
Using the dashboard or chart theme
Your custom chart can be styled dynamically based on the chart or dashboard theme configured by the user. The options object passed to the render() function always contains a theme property that you can use to customize the chart's appearance.
This theme property is of type ThemeConfig (available from the @luzmo/dashboard-contents-types library) and contains following properties.
interface ThemeConfig {
axis?: Record<'fontSize', number> // Font size of the axis labels.
background?: string; // Background color of the dashboard canvas.
borders?: {
'border-color'?: string; // Color of the border
'border-radius'?: string; // Radius of the border
'border-style'?: string; // Style of the border
'border-top-width'?: string; // Top width of the border
'border-right-width'?: string; // Right width of the border
'border-bottom-width'?: string; // Bottom width of the border
'border-left-width'?: string; // Left width of the border
}; // Border styling.
boxShadow?: {
size?: 'S' | 'M' | 'L' | 'none'; // Size of the boxshadow.
color?: string; // Color of the boxshadow.
}; // Box shadow styling.
colors?: string[]; // Custom color palette, an array of colors used when a chart needs multiple colors (e.g. donut chart).
font?: {
fontFamily?: string; // Font family used in the chart.
fontSize?: number; // Font size in px.
'font-weight'?: number; // Font weight.
'font-style'?: 'normal'; // Font style.
}; // Font styling.
itemsBackground?: string; // Background color of the chart.
itemSpecific?: {
rounding?: number; // Rounding of elements in the chart.
padding?: number; // Padding between elements in the chart.
};
legend?: {
type?: 'normal' | 'line' | 'circle'; // Display type of the legend.
fontSize?: number; // Font size of the legend in px.
lineHeight?: number; // Line height of the legend in px.
}; // Legend styling, applied if a legend is displayed.
mainColor?: string; // Main color of the theme.
title?: {
align?: 'left' | 'center' | 'right'; // Alignment of the title
bold?: boolean; // Whether the title is bold
border?: boolean; // Whether the title has a bottom border
fontSize?: number; // Font size of the title in px
italic?: boolean; // Whether the title is italic
lineHeight?: number; // Line height of the title in px
underline?: boolean; // Whether the title is underlined
}; // Title styling, applied if a title is displayed.
tooltip?: {
fontSize?: number; // Font size of the tooltip in px
background?: string; // Background color of the tooltip
lineHeight?: number; // Line height of the tooltip in px
opacity?: number; // Opacity of the tooltip
}; // Tooltip styling, applied if a tooltip is displayed (e.g. on hover over a bar in a bar chart).
}Example usage:
import { ThemeConfig } from '@luzmo/dashboard-contents-types';
// In your chart.ts file
export function render({
container,
data = [],
slots = [],
slotConfigurations = [],
options = {},
language = 'en',
dimensions: { width = 600, height = 400 } = {}
}: ChartParams): void {
// Extract theme from options
const theme: ThemeConfig = options.theme;
// Clear container and set background
container.innerHTML = '';
container.style.backgroundColor = theme.itemsBackground;
// Create main chart container with dynamic theme properties
const chartContainer = document.createElement('div');
chartContainer.className = 'chart-container';
chartContainer.style.fontFamily = theme.font?.fontFamily || 'system-ui, sans-serif';
chartContainer.style.fontSize = (theme.font?.fontSize || 13) + 'px';
// Add a title that uses mainColor
const titleElement = document.createElement('h2');
titleElement.textContent = 'Chart Title';
titleElement.style.color = theme.mainColor;
chartContainer.appendChild(titleElement);
}Styling with chart.css
The chart.css file allows you to add custom styles to your chart elements. The CSS is bundled with your chart and isolated from the dashboard styles.
Example:
.bar-chart-container {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, 'Segoe UI', Roboto, sans-serif;
}
.chart-title {
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: 600;
text-align: center;
}
.axis path,
.axis line {
stroke: #e0e0e0;
}
.axis text {
font-size: 12px;
fill: #666;
}
.bar {
transition: opacity 0.2s;
}
.bar:hover {
opacity: 0.8;
}
.legend-item {
display: inline-flex;
align-items: center;
margin-right: 10px;
font-size: 12px;
}Your CSS will be minified during the build process and included in the final chart package.
Interacting with the Dashboard
Your custom chart can interact with other items in the dashboard by sending events to the parent window. There are two main types of events you can send:
Filter event (setFilter)
Filter events allow your chart to filter data in other dashboard items. The filter structure must match the ItemFilter type from the @luzmo/dashboard-contents-types library.
import { ItemFilter } from '@luzmo/dashboard-contents-types';
// Example of sending a filter event
function sendFilterEvent(filters: ItemFilter[]): void {
const eventData = {
type: 'setFilter', // Must always be 'setFilter'
filters: filters
};
// Post message to parent window
window.parent.postMessage(eventData, '*');
}
// Example usage in a click handler
function onBarClick(category: string, value: number): void {
const filters: ItemFilter[] = [
{
expression: '? = ?', // Filter expression
parameters: [
{
columnId: 'category-column-id', // Column to filter on
datasetId: 'dataset-id' // Dataset containing the column
},
category // Value to filter by
]
}
];
sendFilterEvent(filters);
} The ItemFilter interface has the following structure:
interface ItemFilter {
// Filter expression from a predefined list
expression: '? = ?' | '? != ?' | '? in ?' | '? not in ?' | '? like ?' | '? not like ?' |
'? starts with ?' | '? not starts with ?' | '? ends with ?' | '? not ends with ?' |
'? < ?' | '? <= ?' | '? > ?' | '? >= ?' | '? between ?' | '? is null' | '? is not null';
// Filter parameters
parameters: [
{
columnId?: string; // Column to filter on
datasetId?: string; // Dataset containing the column
level?: number; // Optional level for hierarchical or datetime data
},
any // Value to filter by
];
}Custom event (customEvent)
Custom events allow your chart to send any data from your chart to the dashboard for custom handling. This custom event can then further travel from the dashboard to your own application (if the dashboard is embedded), allowing you to create flexible and powerful workflows in your own application.
The event type must always be 'customEvent', but you can include any data structure you need.
// Example of sending a custom event
function sendCustomEvent(eventType: string, data: any): void {
const eventData = {
type: 'customEvent', // Must always be 'customEvent'
data: {
eventType: eventType, // Your custom event type
...data // Any additional data you want to send
}
};
// Post message to parent window
window.parent.postMessage(eventData, '*');
}
// Example usage in a click handler
function onDataPointClick(category: string, value: number): void {
sendCustomEvent('dataPointSelected', {
category: category,
value: value,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString()
});
}Adding third party libraries
You can install and use third party libraries in your chart. Add them to the package.json file of the custom-chart project and import them in your chart.ts file to start using them.
For example, interesting libraries you can use to develop your chart are:
D3.js
Chart.js
Tanstack Table
...
Building and packaging
Production package
To create a distribution-ready package that can be uploaded to Luzmo:
npm run buildThis command:
Builds the chart
Validates the manifest.json against the schema
Creates a ZIP archive (bundle.zip) containing all required files, ready for upload to Luzmo
Validation only
To validate your manifest.json without building:
npm run validateTroubleshooting
Common issues
Manifest validation errors : Check your slot configuration against the schema
Chart not rendering : Verify your data structure matches what your render function expects
Build errors : Check the console for detailed error messages
Logs and debugging
Builder logs appear with the [ANGULAR] prefix
Bundle server logs appear with the [BUNDLE] prefix
Chart watcher logs appear with the [WATCHER] prefix
Other resources
- Developing a Custom chart
- Introduction
- Quick Start
- Prerequisites
- Installation
- Project structure
- Creating your custom chart
- Key files to modify
- Manifest configuration
- Required properties
- Optional properties
- Slot options properties
- Example Manifest
- Chart implementation
- Core functions
- Chart styling
- Interacting with the Dashboard
- Adding third party libraries
- Building and packaging
- Production package
- Validation only
- Troubleshooting
- Common issues
- Logs and debugging
- Other resources