Set up an Integration
The first step to embed dashboards in your application is setting up an Integration. This can be easily created and maintained from within our application as well as through our API!
Create an Integration
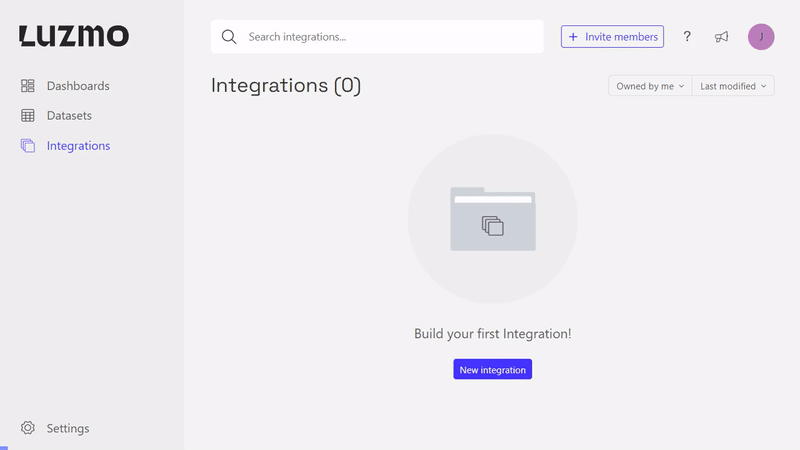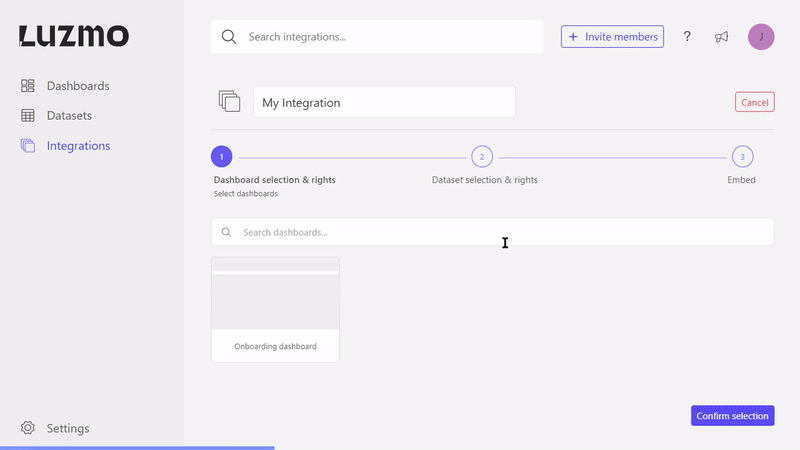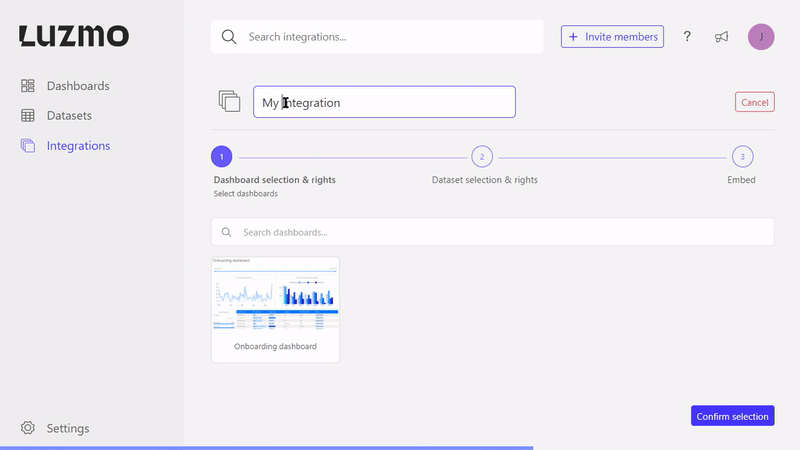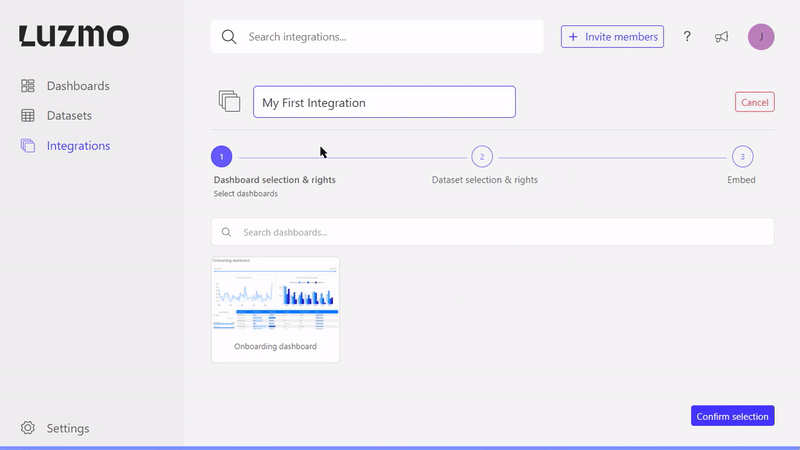
If you're an Organization owner, you can login to Luzmo and on top of the page you will find the Integrations tab. From there you can start the process of creating an Integration by clicking on the New Integration button.
client.create("integration",
{
name: {
en: "< Integration name in English ›",
fr: "< Integration name in French >"
}
}
)
.then(function(integration) {
console.log("Success!", integration);
});Associate dashboards
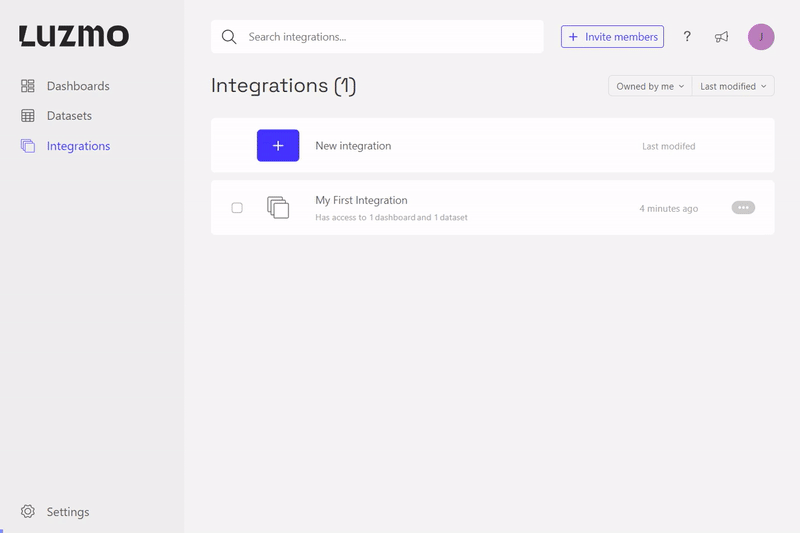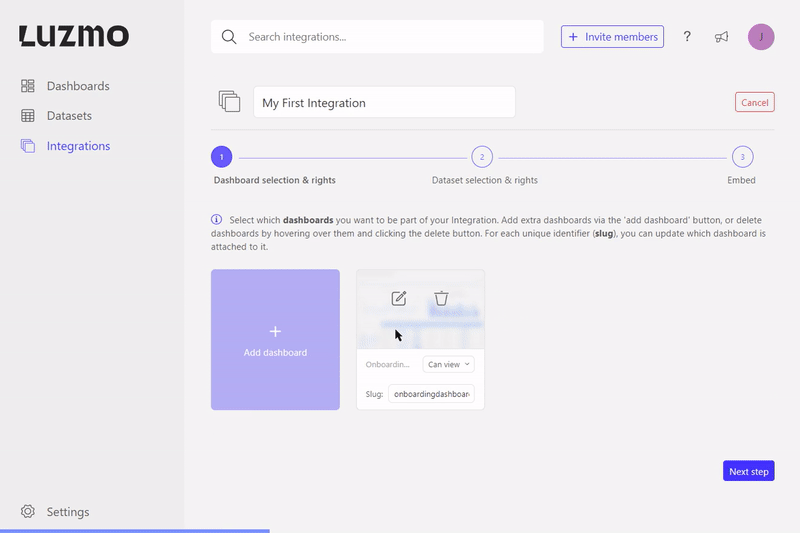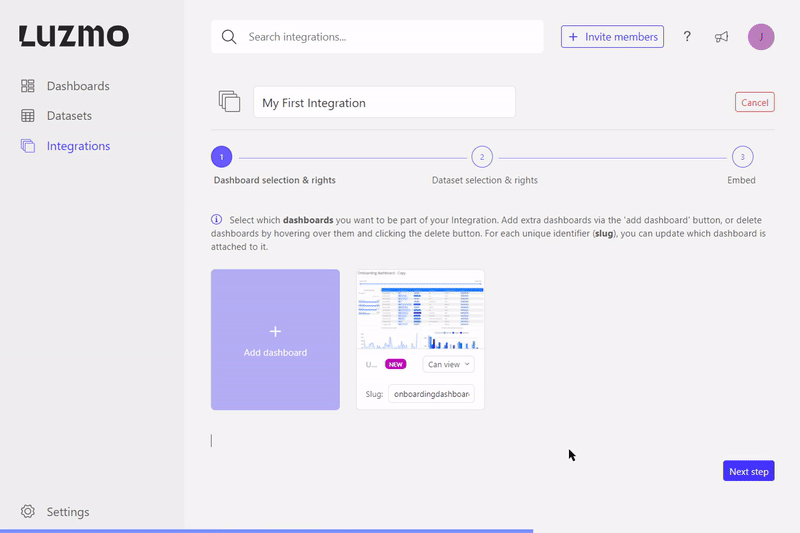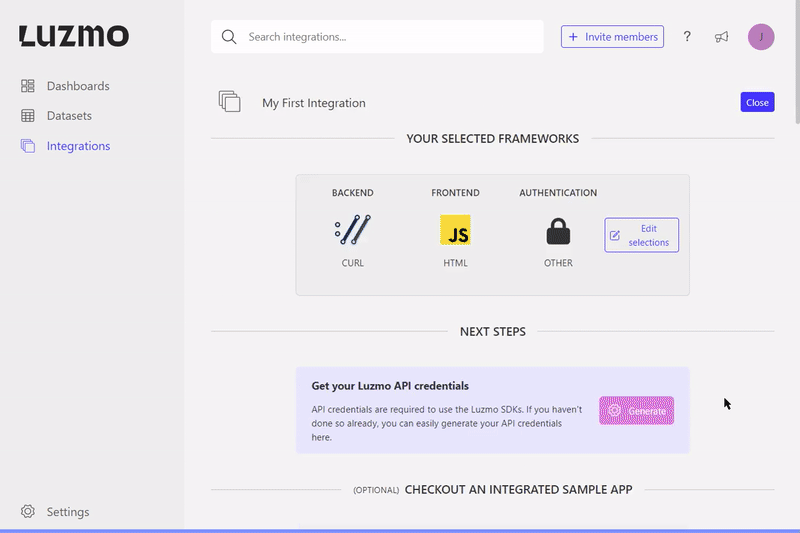
After starting the creation of the Integration, you can select dashboards that should be associated with the Integration together with their access rights. In order to start associating dashboards with an Integration, you already need to be an owner of the dashboard and the Integration. That means that you either created the dashboard or received access from someone that gave you owner access. That way it is possible to set multiple owners for a dashboard.
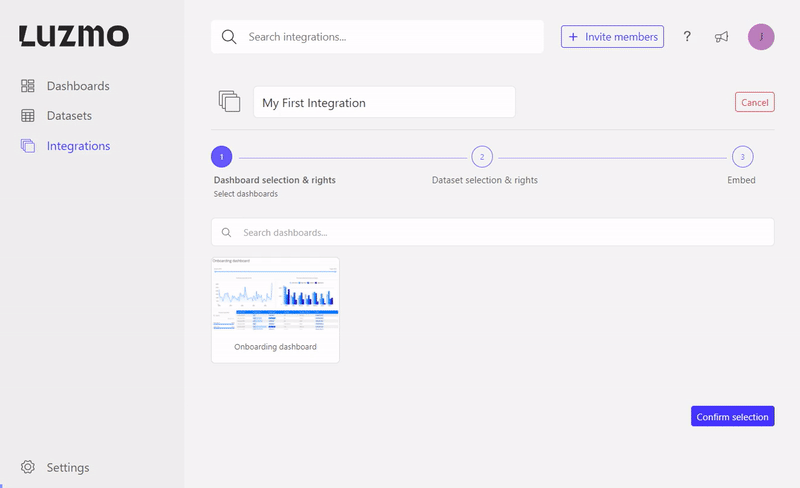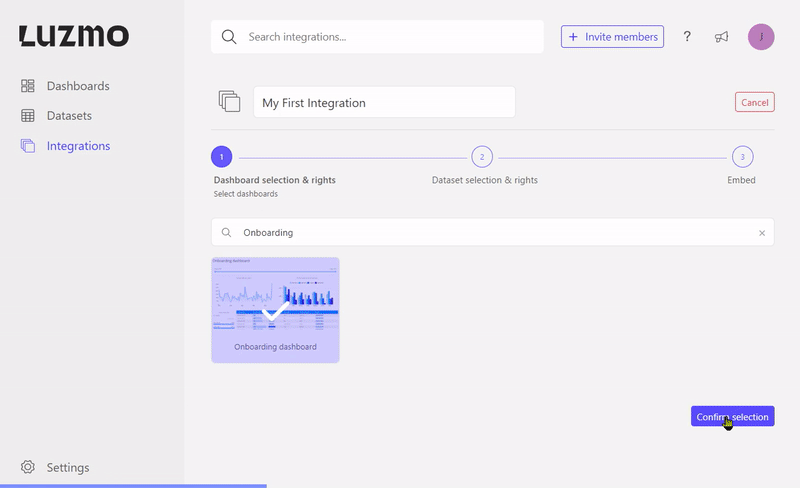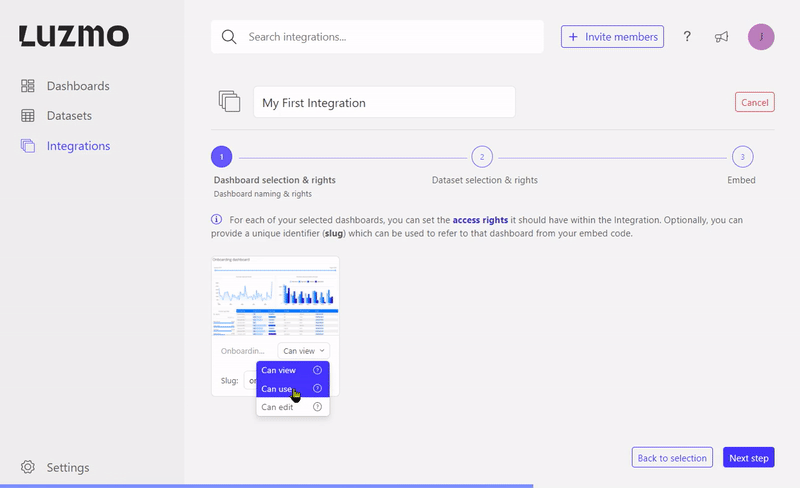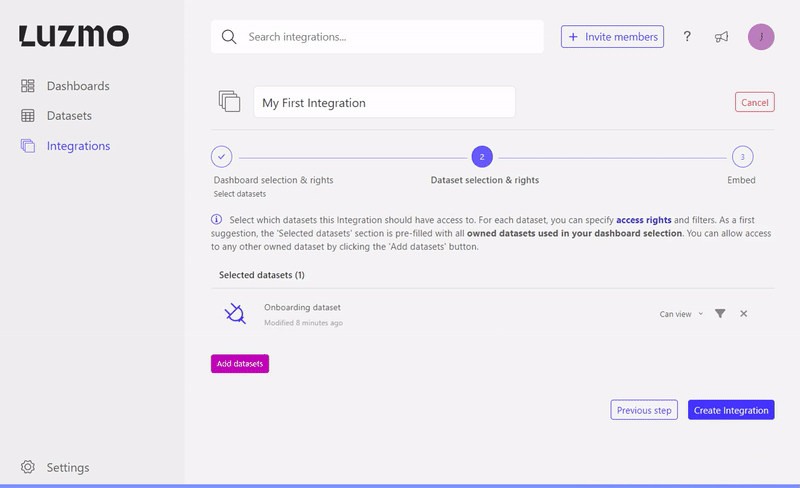
The association has flag properties to define what kind of access the Integration will receive. If no flag properties are specified the Integration will receive "view" access by default. The available flags are:
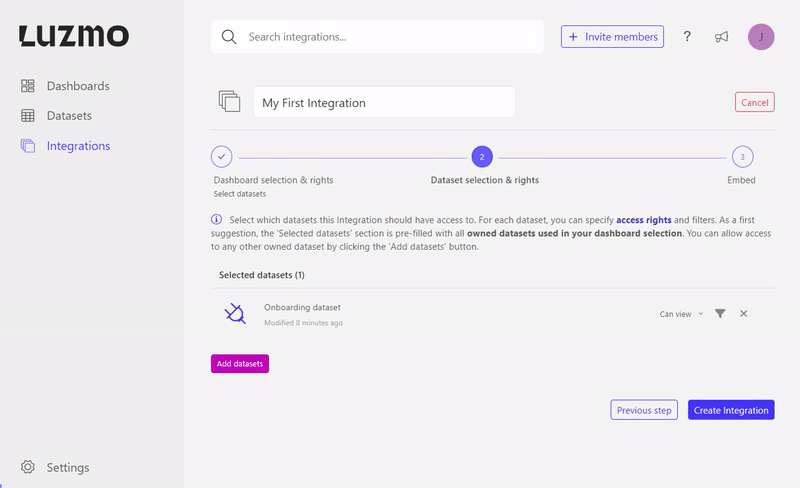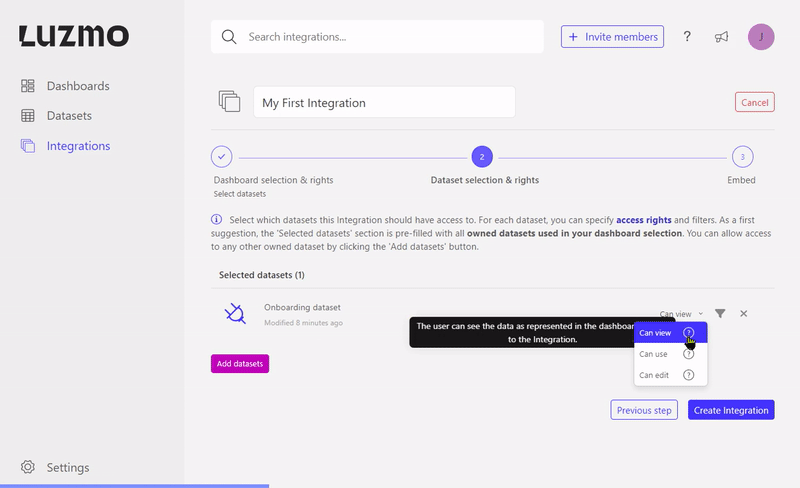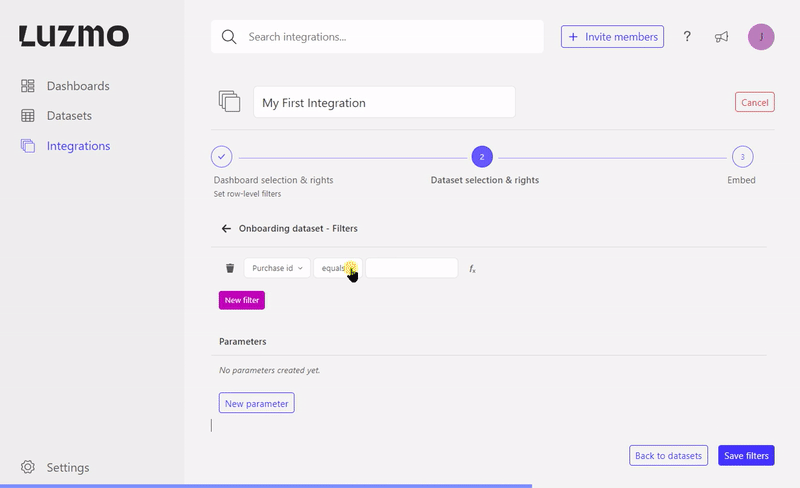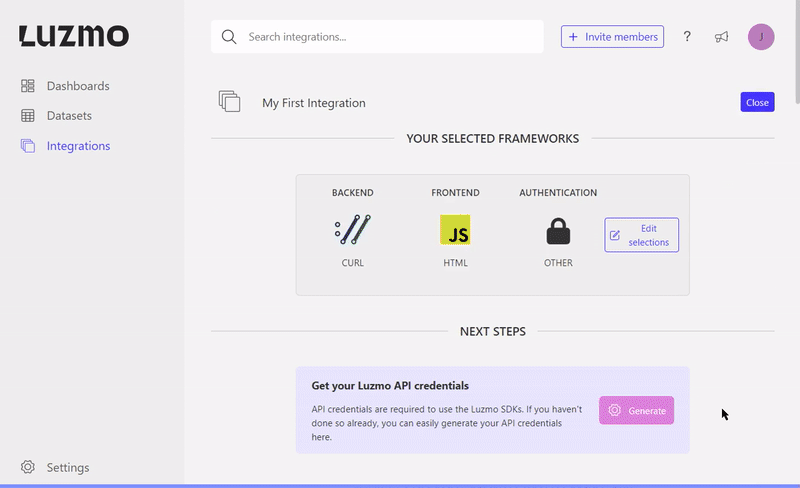
'Can view' (or 'flagRead') - gives the SSO user the right to only view the dashboard.
'Can use' (or 'flagUse') - next to viewing a dashboard, the SSO user is able to create a variant of the dashboard, or duplicate it (only in editMode “editFull”).
'Can edit' (or 'flagModify') - besides viewing and duplicating the dashboard, the SSO user can edit the dashboard itself.
If you give 'can use' or 'can edit' rights on a dashboard, you must ensure that all multi-tenant (parameter) filters are defined on the dataset level (i.e. when associating the dataset(s) with the Integration/Suborganization/Group/User) and not on the dashboard level. Designer users are able to modify the dashboard content (either in a variant, in a duplicate or in the dashboard itself) and thus remove these (parameter) filters!
Next to the flag properties, you can also specify a unique slug that can be used to target the specific dashboard in your frontend (see Step 2: Embed the dashboard ). This is particularly useful if you'd like to replace an embedded dashboard in your application without having to change anything in your application's code! The gif below shows how you can replace a dashboard for a certain slug in our UI.
let promise = client.associate("integration", "< your Integration id >", {
role: "Securables",
id: "< your dashboard id >"
},
{
flagRead: true,
slug: "< lowercase alphanumeric slug name >"
});Associate datasets
When associating a dataset with an Integration you can specify some flag properties to define what kind of access the Integration will receive. If no flag properties are specified the Integration will receive viewing access by default. The available flags are:
'Can view' (or 'flagRead') - users are only allowed to query the dataset in existing dashboard(s) that are accessible to them (i.e. the user is not able to use this dataset when creating/editing a dashboard).
'Can use' (or 'flagUse') - the user is also able to use this dataset when creating or editing a dashboard.
'Can edit' (or 'flagModify') - the user is able to use this dataset when creating or editing a dashboard, and is able to edit the dataset itself (e.g. change column names, create or alter hierarchies, create or alter derived columns, etc.)
For security reasons it’s of uttermost importance that multi-tenant (parameter) filters are specified on the dataset level, this ensures that they are always applied when the user queries the dataset directly or via a (new) dashboard. Parameterizable filters can be used to dynamically apply these filters by overriding the parameter value(s) when requesting a SSO token for your user. Instead of using parameterizable filters, you could also specify static filters when associating a dataset with an Integration or when requesting SSO authorization tokens.
As shown in the gif below, you can additionally specify filters when defining the dataset-Integration association. In case you want to dynamically filter a dataset based on the user logged in in your application, parameter filters are the easiest way of setting this up!
let promise = client.associate("integration", "< your Integration id >", {
role: "Securables",
id: "< your dataset id >"
},
{
flagRead: true
});let promise = client.associate("integration", "< your Integration id >", {
role: "Securables",
id: "< your dataset id >"
},
{
flagRead: true,
filters: [
{
clause: "where",
origin: "global",
securable_id: "< dataset id >",
column_id: "< column id of a column used in the dataset >",
expression: "? in ?",
value: {
parameter: "metadata.< parameter name >",
type: "array[hierarchy]",
value: ["< default parameter value >"]
}
}
]
});